Diff
(add more extensions) |
(add mime type) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|subcat=Archiving | |subcat=Archiving | ||
|extensions={{ext|patch}}, {{ext|diff}}, {{ext|pch}}<ref>https://file-extension.net/seeker/file_extension_pch</ref>, {{ext|dif}}<ref>https://file-extension.net/seeker/file_extension_dif</ref>, {{ext|rej}}<ref>https://file-extension.net/seeker/file_extension_rej</ref> | |extensions={{ext|patch}}, {{ext|diff}}, {{ext|pch}}<ref>https://file-extension.net/seeker/file_extension_pch</ref>, {{ext|dif}}<ref>https://file-extension.net/seeker/file_extension_dif</ref>, {{ext|rej}}<ref>https://file-extension.net/seeker/file_extension_rej</ref> | ||
| + | |mimetypes={{mimetype|text/x-patch}}<ref>https://gitlab.freedesktop.org/xdg/shared-mime-info/-/blob/master/data/freedesktop.org.xml.in freedesktop shared-mime-info database</ref> | ||
|image=Unified diff.png | |image=Unified diff.png | ||
|caption=example of unified diff | |caption=example of unified diff | ||
| Line 41: | Line 42: | ||
* [[Wikipedia:Diff utility]] | * [[Wikipedia:Diff utility]] | ||
* [http://www.gnu.org/software/diffutils/manual/html_node/Output-Formats.html GNU Diffutils manual: Output Formats] | * [http://www.gnu.org/software/diffutils/manual/html_node/Output-Formats.html GNU Diffutils manual: Output Formats] | ||
| − | * [https://linuxacademy.com/blog/ | + | * [https://web.archive.org/web/20190905202025/https://linuxacademy.com/blog/linux/introduction-using-diff-and-patch/ Using diff and patch (archived)] |
| − | * [http://jungels.net/articles/diff-patch-ten-minutes.html The Ten Minute Guide to diff and patch] | + | * [https://web.archive.org/web/20151015015305/http://jungels.net/articles/diff-patch-ten-minutes.html The Ten Minute Guide to diff and patch (archived)] |
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 08:39, 28 December 2023
- For "diff files" in general, see Archiving#Diff files. For Xerox DIFF, see XIFF.
diff is a family of formats associated with the traditional Unix diff utility, especially the GNU implementation of it. It encodes the differences between two files. It is often used in the form of a "patch" file that can be used to convert one file to the other.
Diff is intended for use with text files whose lines are mostly short, such as source code.
Contents |
[edit] Formats
The diff utility can produce several different formats:
[edit] Normal diff
The default format, sometimes called "normal diff", contains just the differences, with no header or context.
[edit] Context diff
diff -c produces Context diff format. It has a header, and some contextual data that often makes it possible to patch files even after they have been modified.
It is characterized by lines with lots of asterisks:
***************
Note that the term "context diff" is sometimes used to mean "any diff format that features context" (which would include Unified diff, a different format).
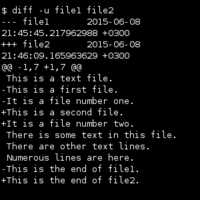
[edit] Unified diff
Main article: Unified diff
diff -u produces Unified diff format. The idea is the same as with Context diff, but the format is more efficient and readable. It is characterized by lines that begin with "@@".
[edit] ed script
diff -e produces a script to be interpreted by the ed text editor. It was used for patch files before the introduction of the patch utility, but has long been obsolete for that purpose.
[edit] Software
- GNU Diffutils:
diff,patch
[edit] Links
- Wikipedia:Diff utility
- GNU Diffutils manual: Output Formats
- Using diff and patch (archived)
- The Ten Minute Guide to diff and patch (archived)